About Blockchain:
- Two main public implementations of blockchain are bitcoin and ethereum. For enterprises and private networks the main two implementations are HyperledgerFabric (more info here) and Ethereum
- Quorum: is an Ethereum-based distributed ledger protocol / platform that supports block chain transactions and contract privacy.
- Consortium: network consensus / multiple organizations maintaining the network. There is a consortium Leader in private blockchain which sets up the initial ether.
- Participants validate and store transactions.
- Data is stored in a ledger, ledger can be updated only by network consensus. Accounts can vote only once.
- Distributed consensus is not a new topic. Products like HDFS, MQ, ZooKeeper / Kafka, Elasticsearch, etc already have implemented this form of data integrity. This approach addresses teh following challenges:
- Crash Fault Tolerance (CFT) algorithms
- Byzantine Fault Tolerance -BFT- (plus Practical BFT)
- Impossibility Triangle (Consistency Availability Partition Tolerenace -CAP- Theorem
- Distributed Consensus Algorithm:
- ZooKeeper uses the Paxos Algorithm.
- R3 Corda and HyperLedger Fabric use the Raft algorithm, now moving to BFT.
- Distributed consensus is not a new topic. Products like HDFS, MQ, ZooKeeper / Kafka, Elasticsearch, etc already have implemented this form of data integrity. This approach addresses teh following challenges:
- Data is stored in a ledger, ledger can be updated only by network consensus. Accounts can vote only once.
- Everyone in the network has an individual identical copy.
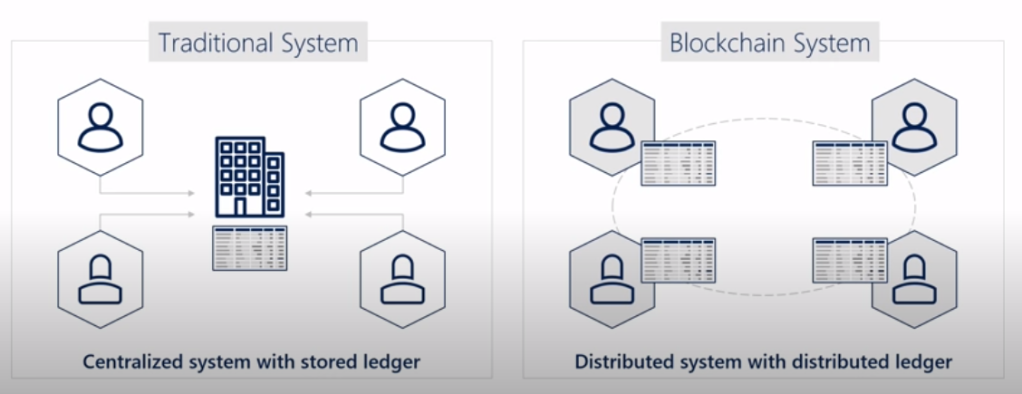
- After a contract is mined (think like deployed and instantiated), you can interact with it.
- «Gas» is what miners are paid for transactions.
- MetaMask: chrome extension to transfer ether between accounts.
- Bitcoin transactions are monetary, in Ethereum is executable code as well.
- Blockchain forms a chain between two blocks using hashes (similar to a single linked list, where first node is called «genesis block» and «root node» in a linked list)
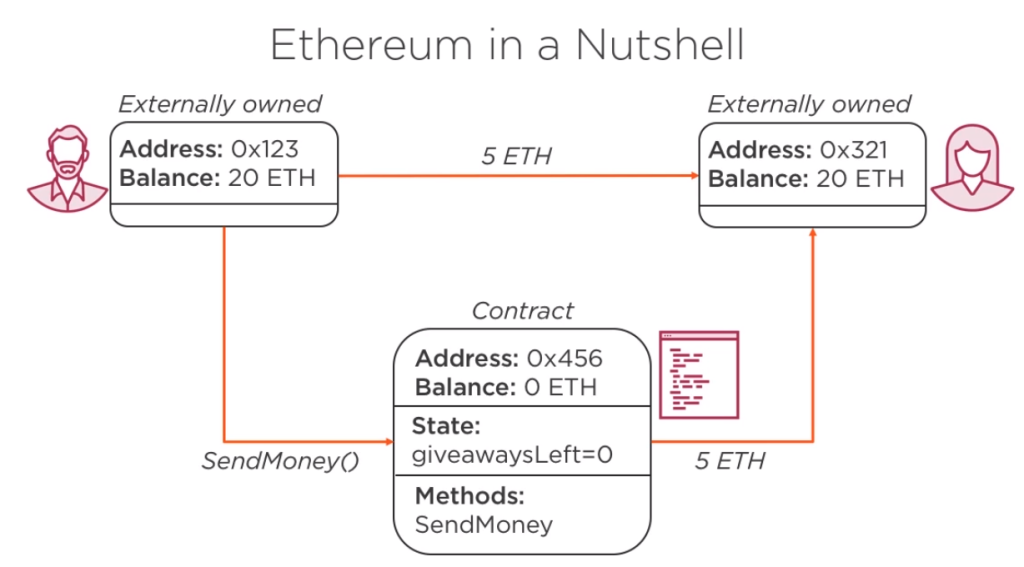
- Distributed Applications (DAPPs): development and deployment approach in blockchain as per below images.
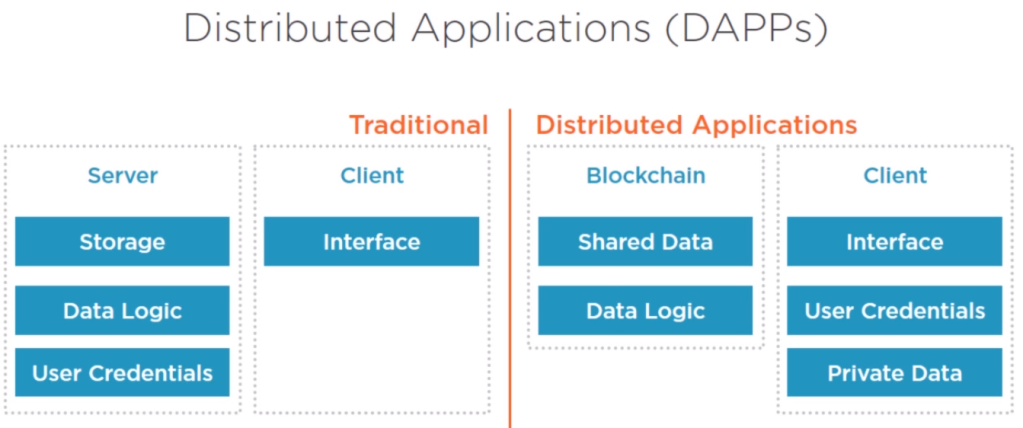
- There are different types of clients for blockchain networks including full nodes, light nodes, and remote clients.
- Ligth nodes don’t download the full blockchain, only the headers to validate the authenticity of the transactions.
- The minimal setup is one transaction node (full node) and 2 validators (light node).
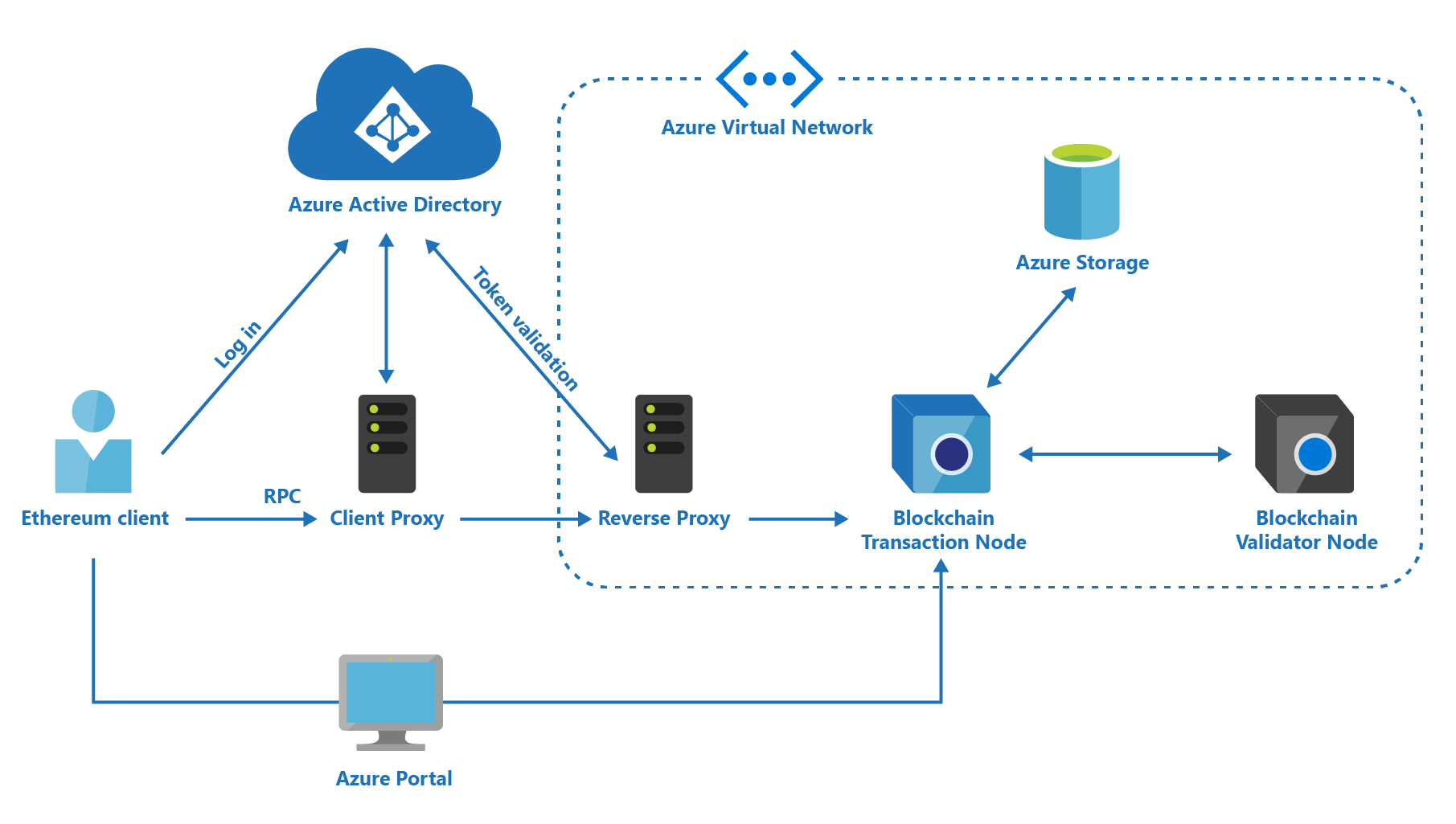
About Dev Tools:
- To build smart contracts the following languages are mainly used: Solidity for Ethereum, Kotlin for Corda and Go for Hyperledger Fabric.
- There are other alternatives to Solidity, e.g.: serpent, viper. Soidity is also supported by Bitcoin.
- These languages compile to ethereum bytecode to run in ethereum nodes
- There are many tools for Smart Contract development, incl.:
- Truffle: set of tools to build, test and assist in smart contract and Dapp development.
- TestRPC: in memory blockchain.
- Ganache/Infura: personal ethereum blockchain to develop locally.
- Hyperledger Besu is a popular Ethereum client
- Remix: testing, debugging and deploying of smart contracts in the browser.
- There are many libraries to interact with an ethereum network, incl.: web3js, nethereum, truffle, etc
About Smart Contract Development
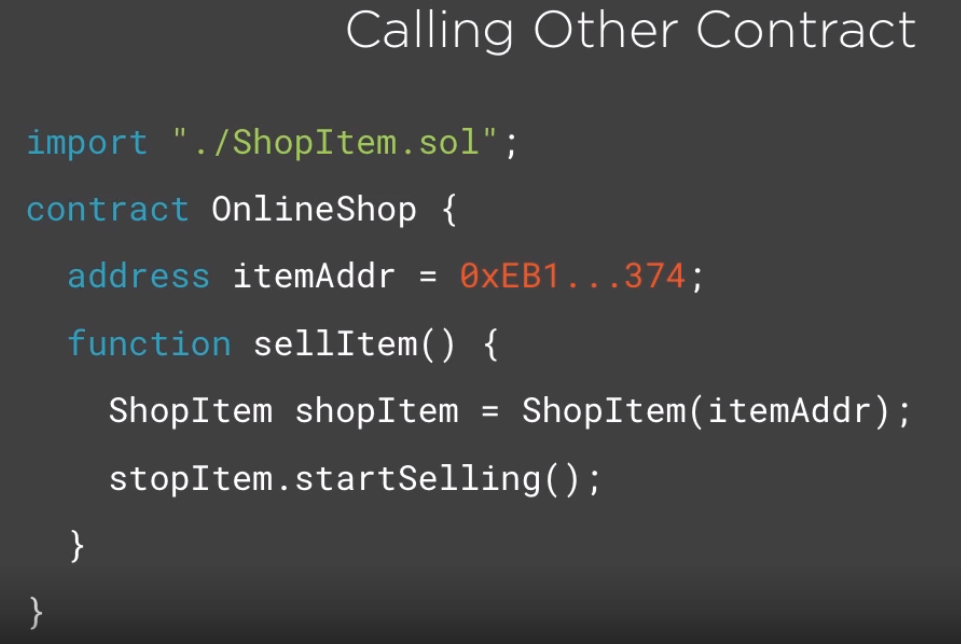
- Contracts have data and methods
- Contrats can interact with people and people between people
- Any participant of the network can call contract functions and change state as per example below.
Thanks for reading,
Javier Caceres
Deja un comentario